Learning Package 9 - COVID-19 Vaccines
| This learning package was created more than a year ago. Please check https://www.moh.gov.sg/covid-19/vaccination for the latest updates on the COVID-19 situation in Singapore. |
Photo credit: https://pixabay.com/photos/vaccine-covid-19-vials-vaccination-5895477/
The outbreak of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, also known as COVID-19, was first detected in China in late 2019. This highly contagious disease, which causes symptoms such as fever, breathing difficulties, cough, lesions on the lungs and in severe cases, dyspnea and respiratory distress syndrome, began to spread rapidly to other parts of the globe prompting an urgent race to develop a vaccine.1
Less than a year after the outbreak, several successful trials on potential COVID-19 vaccine candidates have already taken place. According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), there are currently more than 50 COVID-19 vaccine candidates in clinical trials.2 This is a remarkable achievement, considering that before the COVID-19 pandemic, the fastest time for a vaccine to be developed was four years – the mumps vaccine in the 1960s. Several factors facilitated the development of the COVID-19 vaccines in a short timeframe. These included advances in technology which had sped up the manufacturing processes, the provision of ample funding to facilitate multiple trials and unprecedented support by approving authorities.3
Below is a diagrammatic overview of how the various COVID-19 vaccines work and how they compare with one another:4
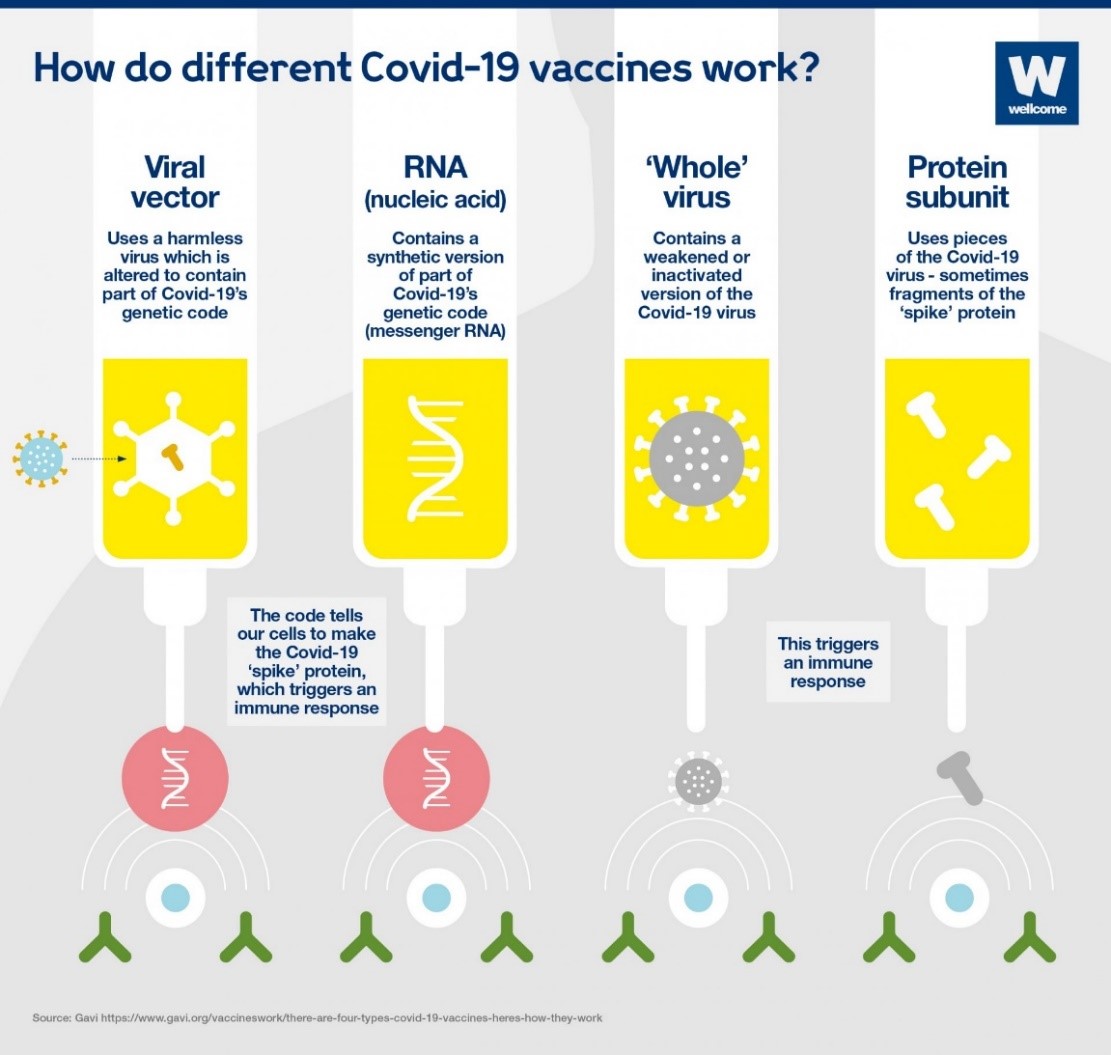
Source: What different types of Covid-19 vaccine are there? (2021, January 8). Wellcome. Retrieved 2021, January 15, from https://wellcome.org/news/what-different-types-covid-19-vaccine-are-there
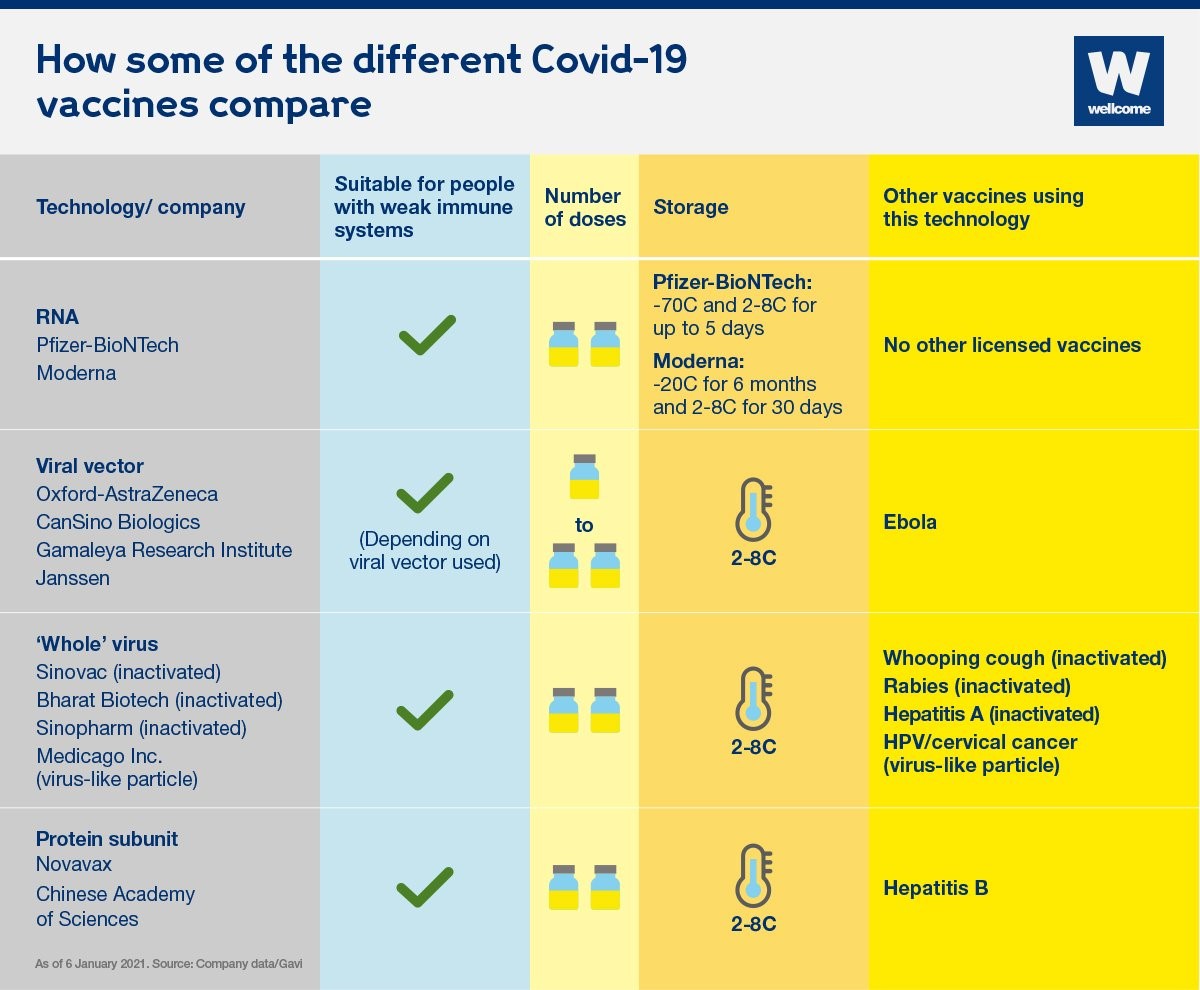
Source: What different types of Covid-19 vaccine are there? (2021, January 8). Wellcome. Retrieved 2021, January 15, from https://wellcome.org/news/what-different-types-covid-19-vaccine-are-there
A range of different vaccines are needed to cater to people of varying age groups, health conditions and geographic locations. An estimated two billion vaccine doses are required to vaccinate high-risk groups around the world by end 2021. To ensure equitable access, the COVID-19 Vaccine Global Access Facility (COVAX) was established to support the research, development and manufacturing of a range of COVID-19 vaccines which would be made available to all participating countries irrespective of their economic status.5
On 2 December 2020, the vaccine developed by American pharmaceutical giant, Pfizer and German biotechnology company, BioNTech was granted emergency-use authorisation by the United Kingdom (UK), which was the first country to kick-start its mass vaccination programme in early December 2020. Other countries in Europe (France, Germany, Denmark, Finland, Hungary, Italy, Poland, Spain, Switzerland), Central and South America (Argentina, Chile, Costa Rica), North America (Canada, United States, Mexico), the Middle East (Israel, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, UAE), the Balkans (Croatia, Greece, Romania), and Russia followed suit. The Pfizer BioNtech and Moderna vaccines were the most frequently administered, along with the Sputnik V vaccine and the Sinovac vaccine.6
Singapore began its mass vaccination programme on 30 December 2020. According to the vaccination strategy proposed by the Expert Committee on COVID-19 vaccination, vaccinations are offered free of charge to all Singaporeans and long-term residents with the aim to complete the vaccinations by the end of 2021. Currently, only the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine has been given the all-clear from the Health Sciences Authority for use in Singapore for individuals aged 16 and above. Priority for the vaccinations will be given to healthcare and frontline workers, the elderly above 70 years and those with underlying health conditions who are more susceptible to complications upon contracting COVID-19.7
As of 20 January 2021, 54.36 million COVID-19 vaccine doses have been administered globally. The US tops the chart at 16.53 million doses administered, followed by China (15 million doses) and the UK (5.44 million doses).8 For now, the vaccines appear to work even for new variants of the coronavirus that were detected in the UK, South Africa and Brazil, although there is heightened urgency for early detection of these virus mutations and to accelerate the mass vaccination programmes.9
Medical professionals advise that mask-wearing, social distancing measures and good hygiene habits such as the frequent washing of hands will have to continue in tandem with vaccinations as the best possible strategy for the containment of the virus.10
To find out more about COVID-19 vaccines and vaccination, check out the resources below.
You can also check out an earlier guide on vaccinations published by the NLB in May 2020 as part of the pandemics learning package: https://mobileapp.nlb.gov.sg/spotlight/pandemics/vaccinations
Videos and Podcasts
1. How vaccines work against COVID-19: Science, simplified
Source: How vaccines work against COVID-19: Science, simplified. (2020, December 18). Scripps Research. Retrieved 2021, January 18.
2. COVID-19 vaccines and herd immunity
Source: COVID-19 vaccines and herd immunity. (2020, December 17). JAMA Network. Retrieved 2021, January 20.
3. Mayo Clinic Q&A podcast: Expert updates on the COVID-19 vaccine
Source: Mayo Clinic Q&A podcast: Expert updates on the COVID-19 vaccine. (2021, January 13). Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 2021, January 18.
4. Why are people hesitant to trust a COVID-19 vaccine?
Source: Why are people hesitant to trust a COVID-19 vaccine? (2020, December 11). ABC News. Retrieved 2021, January 18.
5. Covid-19: Why vaccine mistrust is growing - The Economist
Source: Covid-19: Why vaccine mistrust is growing - The Economist (2020, November 18). The Economist. Retrieved 2021, January 19.
6. Debunking misinformation about COVID-19
Debunking misinformation about COVID-19. (2020, November 13). University of Michigan School of Public Health. Retrieved 2021, January 19.
7. COVID-19 vaccines rolled out at warp speed – safety, side effects and the big logistical challenges
COVID-19 vaccines rolled out at warp speed – safety, side effects and the big logistical challenges. (2021, January 7). Channel News Asia. Retrieved 2021, January 19.
8. Episode #20 - COVID-19 - Variants & Vaccines. (2021, January 8). World Health Organisation
Episode #20 - COVID-19 - Variants & Vaccines. (2021, January 8). World Health Organisation. Retrieved 2021, January 19.
9. Will Covid-19 Vaccine Passports Work?
Source: Will Covid-19 Vaccine Passports Work? (2021, January 17). CNBC. Retrieved 2021, January 18.
10. Singapore's 3 COVID-19 vaccines - and is one better than the others?
Source: Singapore’s 3 COVID-19 vaccines - and is one better than the others? (2021, January 8). CNA Insider. Retrieved 2021, January 21.
Websites
1. What you should know about the COVID-19 vaccine
What you should know about the COVID-19 vaccine. (2020, December 30). Government of Singapore. Retrieved 2021, January 20.
2. COVID-19 vaccines
COVID-19 vaccines. (2021). World Health Organisation. Retrieved 2021, January 20.
3. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Vaccines.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Vaccines. (2020, October 28). World Health Organisation. Retrieved 2021, January 20.
4. Coronavirus Resource Center
Coronavirus Resource Center. (2021, January 15). Harvard Health Publishing. Retrieved 2021, January 19.
5. COVID-19 vaccine: Guidance from the Mayo Clinic
COVID-19 vaccine: Guidance from the Mayo Clinic. (2021). Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 2021, January 20.
Journal articles
1. A strategic approach to COVID-19 vaccine R&D
Corey, L., Mascola, J. R., Fauci, A. S., & Collins, F. S. (2020, May 29). A strategic approach to COVID-19 vaccine R&D. Science, 368 (6494), 948-950. Retrieved 2021, January 15.
2. A global survey of potential acceptance of a COVID-19 vaccine
Lazarus, J. V. [et. al]. (2020, October). A global survey of potential acceptance of a COVID-19 vaccine. Nature Medicine (2020). Retrieved 2021, January 15.
3. The COVID-19 vaccine race: Challenges and opportunities in vaccine formulation
Wang, J. [et. al.]. (2020, August). The COVID-19 vaccine race: Challenges and opportunities in vaccine formulation. AAPS PharmSciTech, 21. Retrieved 2021, January 15.
4. Efforts at COVID-19 vaccine development: Challenges and successes
Haque, A., & Pant, A. B. (2020, December). Efforts at COVID-19 vaccine development: Challenges and successes. Vaccines 2020, 8(4), 739. Retrieved 2021, January 15.
5. Acceptance of a COVID-19 vaccine: A multifactorial consideration
García, L. Y., & Cerda, A. A. (2020, November 10). Acceptance of a COVID-19 vaccine: A multifactorial consideration. Vaccine, 38(48). Retrieved 2021, January 15 from ProQuest Central via NLB’s eResources website. (myLibrary ID is required to access this article.)
Chinese / Malay / Tamil resources
1. 大比拼!全球疫苗比较优势知多少?
联合早报网从研发进度、价格、有效性及副作用等几方面梳理了5款领跑疫苗的长短处。(2020年12月17日)。联合早报网。Retrieved 2021, January 18.
This Lianhe Zaobao article compares the five vaccines that are scheduled to be rolled out in terms of progress, price, effectiveness and possible side effects.
2. 新冠疫苗开打 你应当知道的几大问题
新冠疫苗开打 你应当知道的几大问题(2020年12月17日)。BBC中文网。Retrieved 2021, January 18.
This article published by the BBC Chinese website provides answers to some of the common questions on COVID-19 vaccines.
3. Vaksin Covid-19 akan diberi percuma kepada semua warga: PM Lee
Vaksin Covid-19 akan diberi percuma kepada semua warga: PM Lee. (2020, December, 14). Berita Harian. Retrieved 2021, January 15.
All Singapore citizens and permanent residents will get free vaccination for Covid-19.
4. Bekalan pertama vaksin COVID-19 tiba di S’pura dari Belgium
Bekalan pertama vaksin COVID-19 tiba di S’pura dari Belgium. (2020, December 21). Berita Mediacorp. Retrieved 2021, January 15.
A report on the first batch of the COVID-19 vaccine arriving in Singapore from Belgium.
5. சிங்கப்பூரில் கொவிட்-19 தடுப்பூசி: தெரிந்துகொள்ள வேண்டிய தகவல்கள்
சிங்கப்பூரில் கொவிட்-19 தடுப்பூசி: தெரிந்துகொள்ள வேண்டிய தகவல்கள். (2021, January 9). Tamilmurasu.com. Retrieved 2021, January 20.
Covid-19 vaccinations have started in Singapore for healthcare front-liners and will be progressively rolled out to the elderly and the rest of the population. From safety to efficacy and the nation’s vaccination strategy, this article answers all the key questions.
6. COVID-19 நோய்க்கு எதிரான தடுப்புமருந்துகள் - சவால்கள் என்னென்ன?
COVID-19 நோய்க்கு எதிரான தடுப்புமருந்துகள் - சவால்கள் என்னென்ன? (2020, November 21). Mediacorp News Group. Retrieved 2021, January 18.
Issues related to developing COVID-19 vaccines such as bottlenecks in vaccine development, possible vaccine candidates, different vaccine strategies, safety evaluation issues, and vaccine production processes are explored here.
Disclaimer/ Rights statement
The information in this resource guide is valid as at January 2021 and correct as far as we are able to ascertain from our sources. It is not intended to be an exhaustive or complete history on the subject. Please contact the Library for further reading materials on the topic.
All Rights Reserved. National Library Board Singapore 2021.
References
-
Zhu, H., Wei, L. & Niu, P. (2020, March 2). The novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. Global Health Research and Policy, 5(6). Retrieved 2021, January 14, from https://ghrp.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s41256-020-00135-6#citeas; Ledford, H., Cyranoski, D. & Van Noorden, R. (2020, December 3). The UK has approved a COVID vaccine − here’s what scientists now want to know. Nature. Retrieved 2021, January 14, from https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-020-03441-8 ↩
-
COVID-19 vaccines. (2021, January). World Health Organisation. Retrieved 2021, January 24, from https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/covid-19-vaccines ↩
-
Ball, P. (2020, December 18). The lightning-fast quest for COVID vaccines − and what it means for other diseases. Nature. Retrieved 2021. January 14, from https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-020-03626-1; Brothers, W. (2020, December 3). A timeline of COVID-19 vaccine development. BioSpace. Retrieved 2021, January 18, from https://www.biospace.com/article/a-timeline-of-covid-19-vaccine-development/ ↩
-
What different types of Covid-19 vaccine are there? (2021, January 8). Wellcome. Retrieved 2021, January 15, from https://wellcome.org/news/what-different-types-covid-19-vaccine-are-there ↩
-
Weller, C. (2020, November 20). Four reasons why we need multiple vaccines for Covid-19. Wellcome. Retrieved 2021, January 15, from https://wellcome.org/news/four-reasons-why-we-need-multiple-vaccines-covid-19 ↩
-
Which countries have rolled out COVID vaccine? (2020, December 24). Al Jazeera Media Network. Retrieved 2021, January 15, from https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2020/12/24/vaccine-rollout-which-countries-have-started ; Hood, M. (2021, January 6). Covid vaccine rollout urgent as new strains take hold. AFP News. Retrieved 2021, January 14, from https://sg.news.yahoo.com/covid-vaccine-rollout-urgent-strains-134117229.html ↩
-
Government accepts recommendations of expert committee on COVID-19 vaccination. (2020, December 27). Ministry of Health. Retrieved 2021, January 18, from https://www.moh.gov.sg/news-highlights/details/government-accepts-recommendations-of-expert-committee-on-covid-19-vaccination ↩
-
COVID-19 vaccine doses administered. (2021, January 21). Our World in Data. Retrieved 2021, January 22, from https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/cumulative-covid-vaccinations?tab=chart&yScale=log&stackMode=absolute®ion=World ↩
-
Kupferschmidt, K. (2021, January 15). New coronavirus variants could cause more reinfections, require updated vaccines. American Association for the Advancement of Science. Retrieved 2021, January 18, from https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2021/01/new-coronavirus-variants-could-cause-more-reinfections-require-updated-vaccines; Khalik, S. (2021, January 18). Experts in Singapore divided on effect of new Covid-19 strains in virus fight. The Straits Times. Retrieved 2021, January 18, from https://www.straitstimes.com/singapore/experts-divided-on-effect-of-new-strains-on-effort-to-curb-virus ↩
-
Frequently asked questions about COVID-19 vaccination. (2021, January 15). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 2021, January 18, from https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/faq.html; Szabo, L. (2021, January 15). 5 reasons to wear a mask even after you’re vaccinated. Kaiser Family Foundation. Retrieved 2021, January 18, from https://khn.org/news/article/5-reasons-to-wear-a-mask-even-after-youre-vaccinated/; Coronavirus Resource Center. (2021, January 15). Harvard Health Publishing. Retrieved 2021, January 19, from https://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/coronavirus-resource-center ↩

